Live camera edge detection
Visualize the OpenCV Canny Edge Detection results from a live camera stream.
Used Rerun types used-rerun-types
Background background
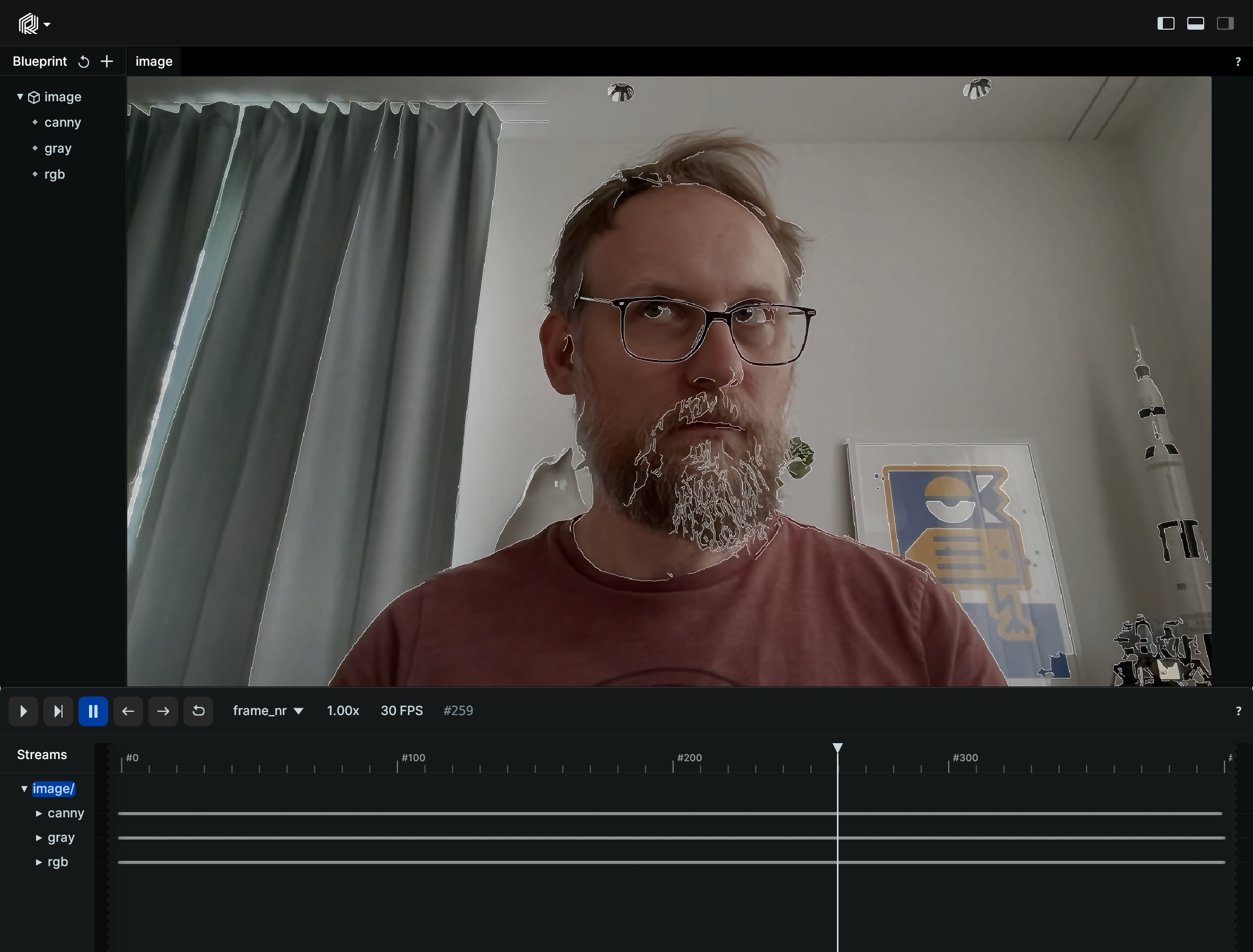
In this example, the results of the OpenCV Canny Edge Detection algorithm are visualized. Canny Edge Detection is a popular edge detection algorithm, and can efficiently extract important structural information from visual objects while notably reducing the computational load. The process in this example involves converting the input image to RGB, then to grayscale, and finally applying the Canny Edge Detector for precise edge detection.
Logging and visualizing with Rerun logging-and-visualizing-with-rerun
The visualization in this example were created with the following Rerun code:
RGB image rgb-image
The original image is read and logged in RGB format under the entity "image/rgb".
# Log the original image
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
rr.log("image/rgb", rr.Image(rgb))Grayscale image grayscale-image
The input image is converted from BGR color space to grayscale, and the resulting grayscale image is logged under the entity "image/gray".
# Convert to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rr.log("image/gray", rr.Image(gray))Canny edge detection image canny-edge-detection-image
The Canny edge detector is applied to the grayscale image, and the resulting edge-detected image is logged under the entity "image/canny".
# Run the canny edge detector
canny = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 200)
rr.log("image/canny", rr.Image(canny))Run the code run-the-code
To run this example, make sure you have the Rerun repository checked out and the latest SDK installed:
pip install --upgrade rerun-sdk # install the latest Rerun SDK
git clone git@github.com:rerun-io/rerun.git # Clone the repository
cd rerun
git checkout latest # Check out the commit matching the latest SDK releaseInstall the necessary libraries specified in the requirements file:
pip install -e examples/python/live_camera_edge_detectionTo experiment with the provided example, simply execute the main Python script:
python -m live_camera_edge_detection # run the exampleIf you wish to customize it, explore additional features, or save it use the CLI with the --help option for guidance:
python -m live_camera_edge_detection --help